Table 1. ICD-9-CM Stroke Codes
| Code | Diagnosis |
| 430 | Subarachnoid hemorrhage |
| 431 | Intracerebral hemorrhage |
| 432 | Other and unspecified intracerebral hemo ... |
| 433 | Occlusion and stenosis of precerebral ar ... |
How to code ICD 9?
Billable Medical Code for Acute, but Ill-Defined, Cerebrovascular Disease Diagnosis Code for Reimbursement Claim: ICD-9-CM 436. Code will be replaced by October 2015 and relabeled as ICD-10-CM 436. The Short Description Is: Cva. Known As
What is the CPT code for stroke?
11 rows · Aug 01, 1998 · ICD-9-CM Stroke Codes. Code Diagnosis; 430: Subarachnoid hemorrhage: 431: Intracerebral ...
What is ICD 9 code for chronic ischemic heart disease?
Stroke 434.91 embolic 434.11 434.10 ICD9Data.com 434.9 ICD-9-CM codes are used in medical billing and coding to describe diseases, injuries, symptoms and conditions. ICD-9-CM 434.11 is one of thousands of ICD-9-CM codes used in healthcare.
What is the ICD 9 code for severe COPD?
Jul 25, 2012 · For the more restrictive code set for stroke/TIA, we included ICD-9 codes 433.x1 and 434.x1 identified from acute inpatient records, as these codes have been found to have high specificity and positive predictive value . Also included in the restrictive set is 435.x for TIA.
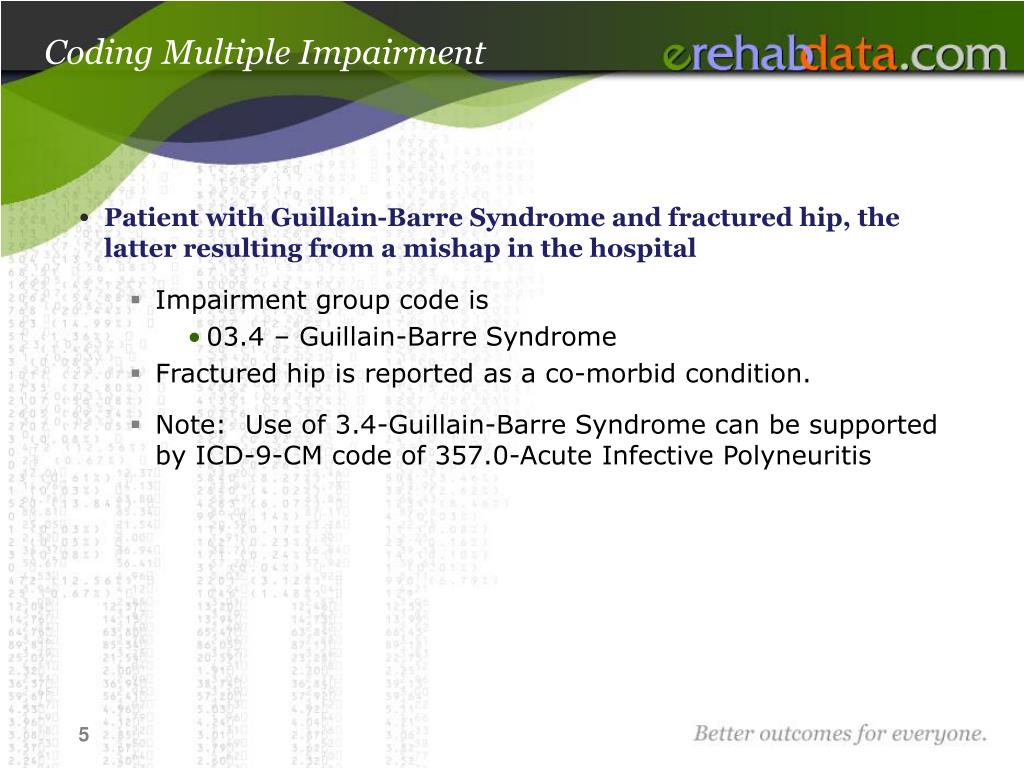
What is the ICD-9 code for CVA?
What is the ICD-10 code for old stroke?
How do you code an ischemic stroke?
How long can you code a stroke?
What is icd10 code for stroke?
What is the CPT code for stroke?
What classification of disease is a stroke?
...
ROSIER scale.
Is Ischemic Stroke?
Is a cerebral infarction a stroke?
When do you code acute stroke?
Is a CVA a stroke?
Subjects and Methods
Available hospital charts for all patients discharged from the Durham Veterans Affairs Medical Center between May 1995 and June 1997 with ICD-9-CM codes 433, 434, and 436 listed in the primary position were reviewed by the investigator (n=175 of 198, 88%).
Results
Of the 175 reviewed cases, 61% (n=106) had an acute ischemic stroke, and the remaining patients (n=69, 39%) had other conditions. The most common other reasons for hospitalization are given in Table 2. Over 50% of the patients with conditions other than ischemic stroke were hospitalized for cerebral angiography or carotid endarterectomy.
Discussion
Despite the use of modifier codes, approximately 15% to 20% of patients with the indicated primary ICD-9-CM discharge codes had conditions other than acute ischemic stroke. As has been reported previously, 5 the highest proportion of nonstroke diagnoses had discharge code 433, and less than 2% of these patients had an acute stroke.
Footnotes
Correspondence to Larry B. Goldstein, MD, Box 3651, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, NC 27710. E-mail [email protected]
What is the ICD-10 code for stroke?
Explicitly document findings to support diagnoses of › Stroke sequela codes (ICD-10 category I69.-) should acute stroke, stroke and subsequent sequela of be used at the time of an ambulatory care visit stroke, and personal history of stroke without sequela, oce, which is considered subsequent to any acute
What is the term for a stroke that occurs when there is disruption of blood flow to brain tissue?
stroke occurs when there is disruption of blood flow to brain tissue, this leads to ischemia (deprivation of oxygen) and potentially infarction (dysfunctional scar tissue). Strokes can be either hemorrhagic, or embolic/thrombotic. Hemorrhagic strokes occur as a result of a ruptured cerebral blood vessel. Embolic/thrombic strokes occur as a result of an obstructed cerebral vessel.
How is a stroke classified?
Stroke is classified by the type of tissue necrosis, such as the anatomic location, vasculature involved, etiology, age of the affected individual, and hemorrhagic vs. Non-hemorrhagic nature. (from Adams et al., Principles of Neurology, 6th ed, pp777-810) A stroke is a medical emergency.
What is the cause of a stroke?
In medicine, a loss of blood flow to part of the brain, which damages brain tissue. Strokes are caused by blood clots and broken blood vessels in the brain. Symptoms include dizziness, numbness, weakness on one side of the body, and problems with talking, writing, or understanding language.
What is the term for a loss of blood flow to the brain?
An ischemic condition of the brain, producing a persistent focal neurological deficit in the area of distribution of the cerebral arteries. In medicine, a loss of blood flow to part of the brain, which damages brain tissue. Strokes are caused by blood clots and broken blood vessels in the brain.
What is the ICD-10 code for stroke?
In ICD-10 CM, code category I63 should be utilized when the medical documentation indicates that an infarction or stroke has occurred. Coding of sequelae of stroke and infarction also demands a level of detail often missing in medical records. There are specific codes which indicate the cause of the infarction, such as embolism or thrombosis, as well as the specific affected arteries. The sixth digit provides additional information which designates the affected side when applicable.
What is the ICD-10 code for cerebral infarction?
The patient is admitted into hospital and diagnosed with cerebral infarction, unspecified ( ICD-10 code I63.9). At the 3-week post-discharge follow-up appointment for the cerebral infarction, the office visit note states the patient had a stroke and has a residual deficit of hemiplegia, affecting the right dominant side.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for granuloma of lymph node
- 2. icd 10 code for left subcapital hip fracture
- 3. icd 10 code for adhd severe senile osteoporosis
- 4. icd code for history of pyelonephritis
- 5. icd 10 code for lateral meniscus tear left knee new inj
- 6. icd 10 code for famil histroy of dm
- 7. icd 10 cm code for chronic arteriosclerotic nephritus, stage 2 ckd
- 8. icd 9 code for routine screening mammogram
- 9. icd 10 code for z01.818
- 10. icd 10 code for sternoclavicular arthritis